Procalcitonin to C-reactive protein ratio is associated with short-term mortality in ischemic stroke patients: preliminary report
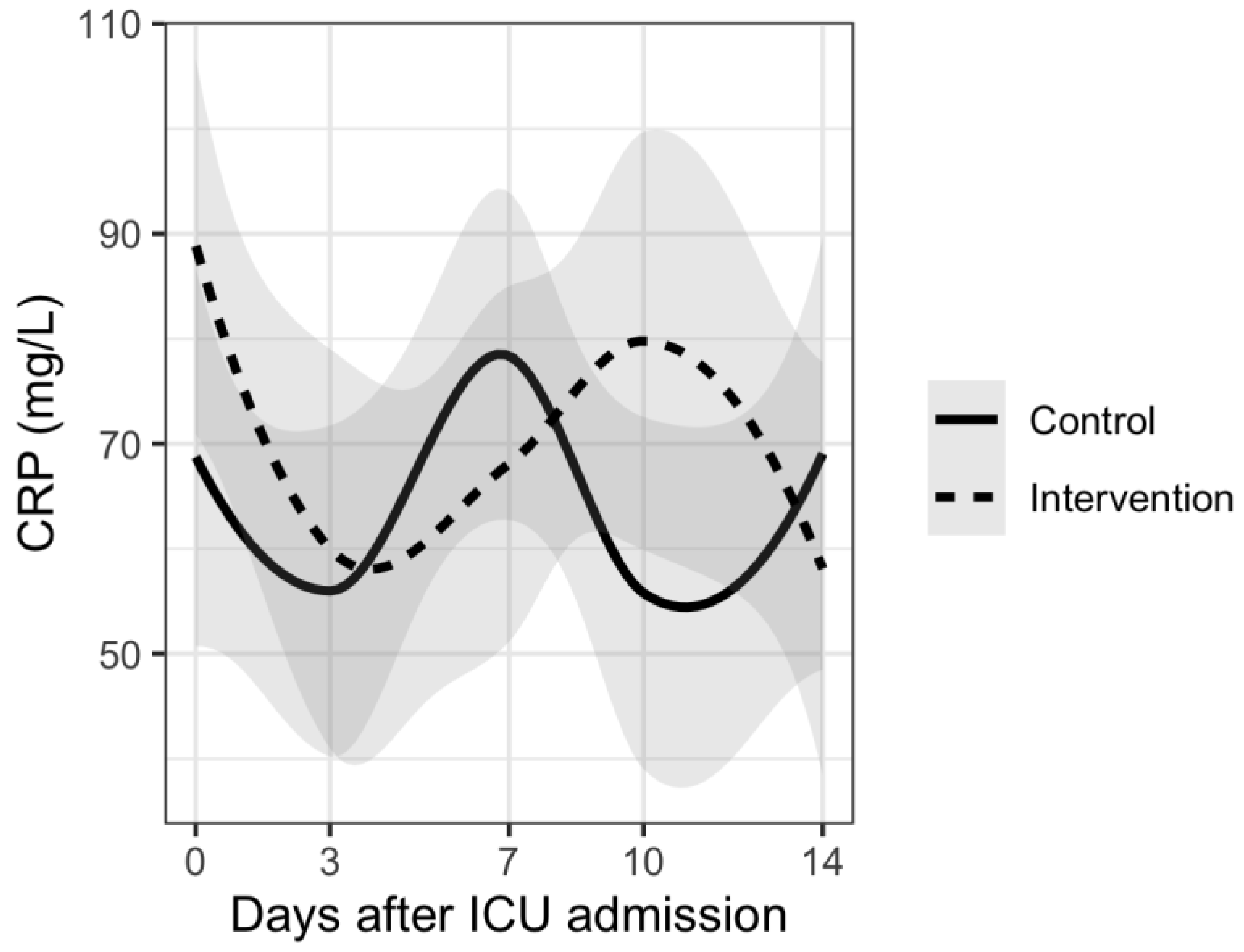
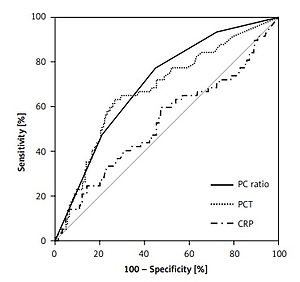
Introduction: Inflammation is associated with the development and progression of ischemic stroke. In this study, we tested the diagnostic ability of procalcitonin (PCT) to C-reactive protein (CRP) ratio (PC ratio; ×10 -6 ) to predict 90-day mortality in ischemic stroke patients. Material and
Prediction of 72-hour mortality in patients with extremely high serum C-reactive protein levels using a novel weighted average of risk scores

C-reactive protein-albumin ratio and procalcitonin in predicting intensive care unit mortality in traumatic brain injury

Kaplan‐Meier survival curves according to procalcitonin (PCT) at

Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Ischemic Stroke Prognosis

Optimal time point for neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio to predict stroke- associated pneumonia

Full article: The role of high high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels at admission on poor prognosis after acute ischemic stroke

High-sensitivity C-reactive protein in stroke patients – The importance in consideration of influence of multiple factors in the predictability for disease severity and death

Potential usefulness of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin determination in patients admitted for neurological disorders in rural Democratic Republic of Congo
Diseases, Free Full-Text

Correlations of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, fibrinogen/albumin
Frontiers Exploring the diagnostic value of CLR and CPR in differentiating Kawasaki disease from other infectious diseases based on clinical predictive modeling

Procalcitonin to C-reactive protein ratio is associated with short-term mortality in ischemic stroke patients: preliminary report